A comprehensive furniture quality inspection checklist serves as the primary safeguard against procurement failure, ensuring that every unit in a high-volume shipment meets established safety and aesthetic standards. Organizations often encounter the significant problem of receiving bulk consignments that appear satisfactory on the surface but harbor deep-seated structural defects or material inconsistencies. This lack of oversight agitates operational workflows, leading to costly logistical reversals, brand erosion, and potential liability risks when substandard items reach the end-user.
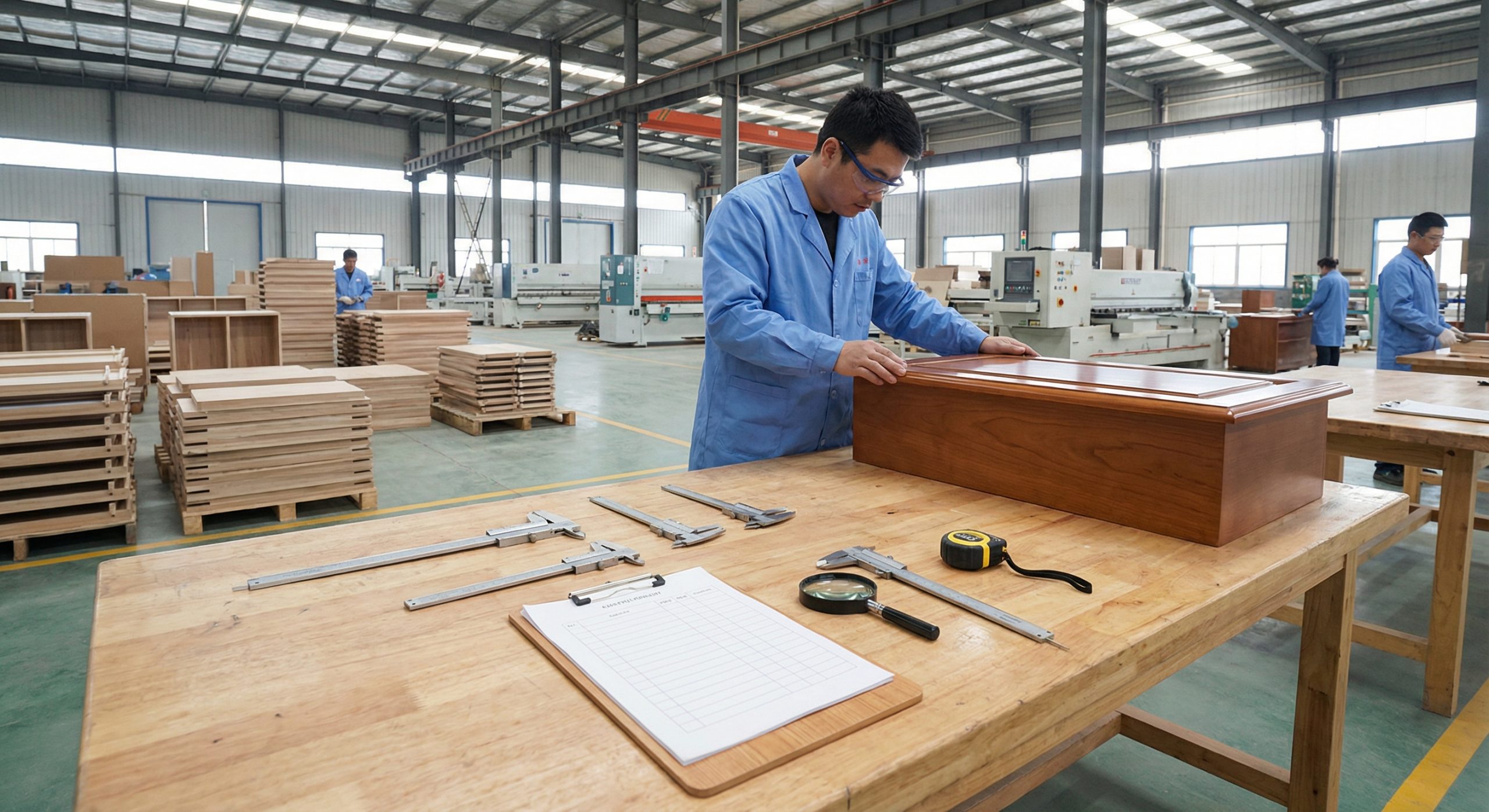

I. Defining the Furniture Quality Inspection Checklist
How does the checklist prevent defects?
A structured verification process identifies deviations from the approved prototype before the cargo departs the factory floor. By documenting every specific requirement, from joinery tension to moisture content, the inspector ensures that mass-produced items do not drift from the original engineering specifications.
- Identification of “critical,” “major,” and “minor” defects.
- Verification of material density and grain alignment.
- Assessment of hardware fastening torque.
When should the checklist be implemented?
Timing is everything in quality control, and the checklist must be utilized at several stages to be truly effective. Early intervention during the “Initial Production Check” prevents the replication of errors across the entire batch, while a “Final Random Inspection” confirms the readiness of the total volume.
- During raw material sourcing to confirm timber or metal grade.
- At the 20% completion mark to catch assembly line errors.
- Pre-shipment to validate final packaging and labeling.
Who manages the verification process?
A neutral third-party entity or an in-house specialized team must execute the formal checklist to eliminate bias while internal factory staff conduct routine checks. Professional inspectors possess the calibrated tools and objective perspective necessary to challenge factory claims regarding durability and compliance.
- Certified quality assurance engineers.
- Independent third-party inspection agencies.
- Procurement lead with specialized technical training.
Key Takeaway: The foundation of a reliable procurement strategy rests on a clearly defined verification document that bridges the gap between design intent and manufacturing reality.
| Inspection Stage | Primary Focus | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Production | Material Specs | Verify raw inputs match samples |
| During Production | Assembly Logic | Ensure consistent construction methods |
| Pre-Shipment | Finished State | Final verification of aesthetics and function |
The following analysis explores the fundamental necessity of defining these stages to prevent the systemic accumulation of manufacturing errors that often plague large-scale furniture production runs.
II. Essential Standards for Bulk Furniture Orders
Seating products must adhere to rigorous mechanical tests to ensure they do not fail under repeated stress or sudden impact. Standards like BIFMA for office furniture or EN 1728 for domestic chairs provide a technical framework for evaluating the endurance of frames and backrests.
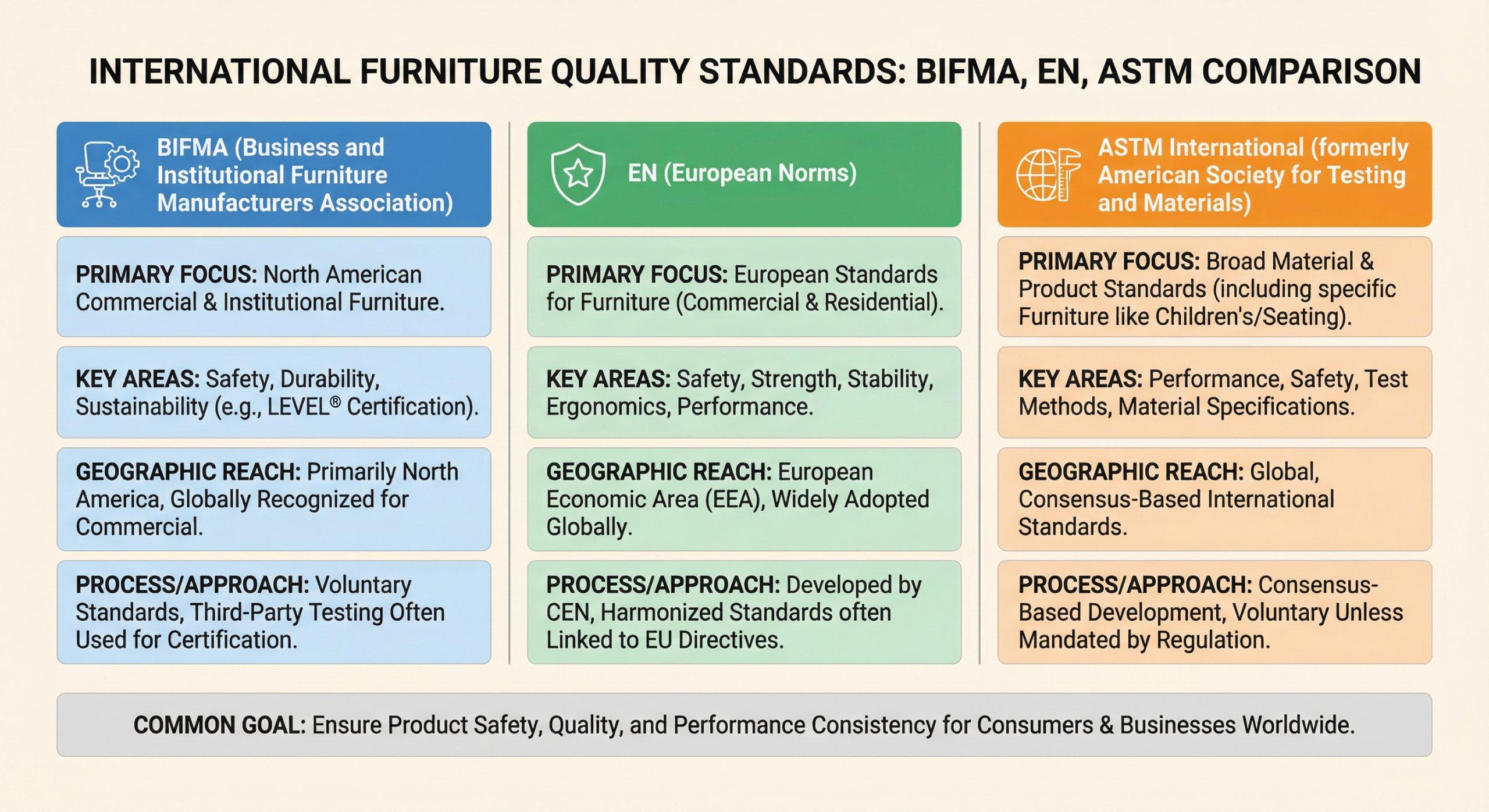
Which global standards apply to seating?
International frameworks like BIFMA X5.1 and EN 1728 define the mechanical requirements for general-purpose office chairs and domestic seating. These protocols involve endurance testing of backrests and stability measurements to prevent tipping during use.
- BIFMA X5.1 for general-purpose office chairs.
- EN 1022 for determination of stability.
- BS EN 581-2 for outdoor seating requirements.
How is stability assessed for cabinetry?
Stability is a non-negotiable safety metric, particularly for taller storage units that pose a tipping risk in residential or commercial environments. Testing protocols involve applying horizontal force to open drawers or doors to simulate real-world usage and prevent accidents.
- ASTM F2057 for clothing storage units.
- EN 14749 for domestic and kitchen storage.
- Load-bearing tests for internal shelving units.
What defines compliance for office desks?
Workstation durability is measured by its ability to withstand static loads and the friction caused by sliding equipment across the surface. Compliance with EN-1335 or similar frameworks ensures that the height-adjustable mechanisms and cable management systems remain functional over years of use.
- Top-load testing for heavy hardware support.
- Cyclic testing of drawer slides and hinges.
- Surface resistance to heat and chemical spills.
Key Takeaway: Adherence to international standards provides a legal and technical safety net that protects both the importer and the end consumer from product failure.
| Standard Code | Furniture Category | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| BIFMA X5.1 | Office Seating | Durability, safety, and structural integrity |
| EN 1728 | Domestic Furniture | Strength and durability of seating |
| ASTM F2057 | Storage Units | Tip-over prevention and stability |
This structured approach to compliance ensures that every item in a bulk order meets the baseline requirements for global market entry and long-term user safety.
III. Material Integrity in the Furniture Quality Inspection Checklist
Excessive moisture in wood leads to warping, cracking, and mold growth once the furniture enters a different climate zone. Using a calibrated moisture meter, inspectors must check multiple points on a piece to ensure the levels fall within the industry-standard range of 8% to 12%.
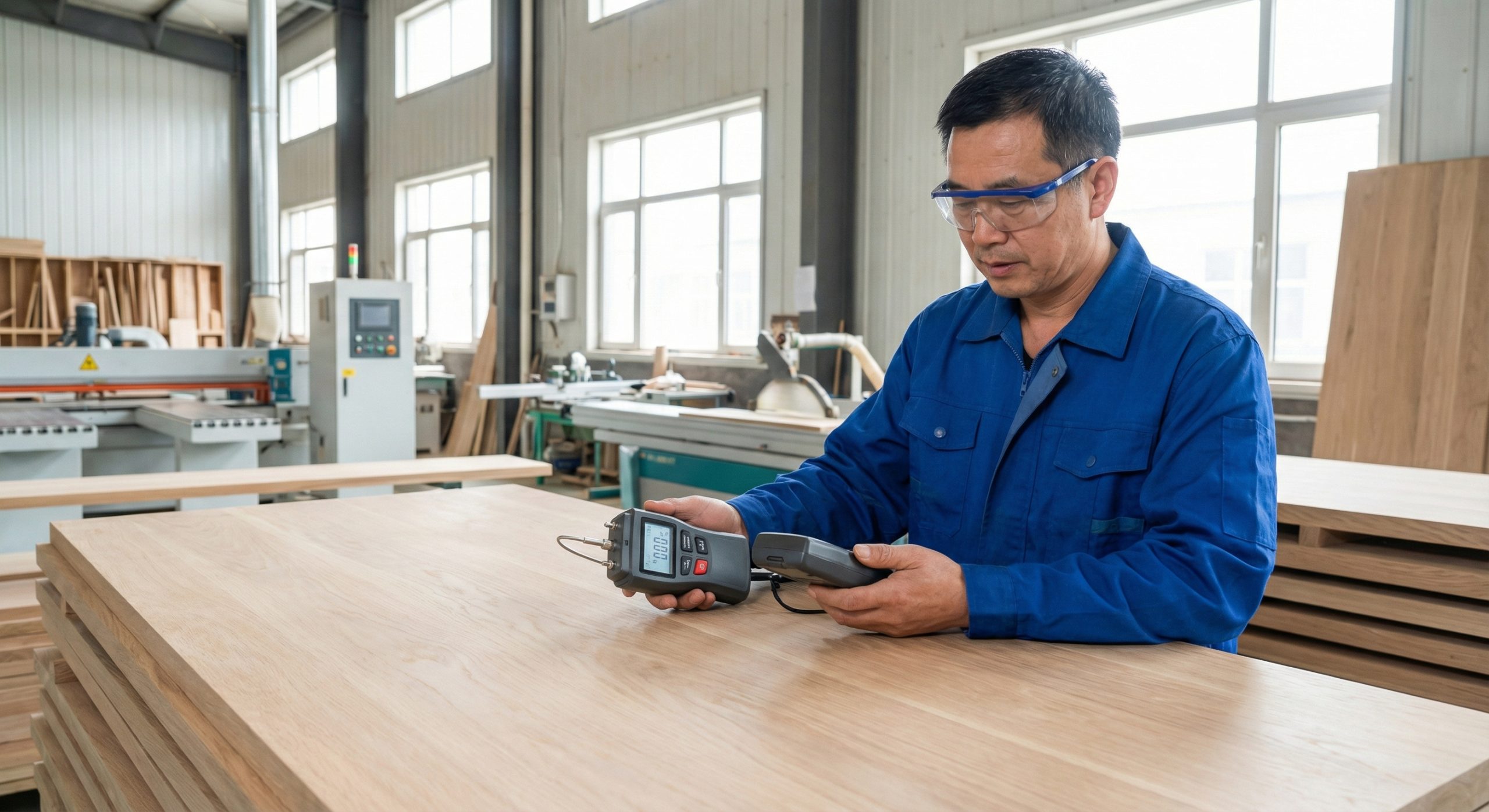

How is moisture content verified in timber?
Digital pin-type moisture meters provide precise readings at various points on components like legs and tabletops. This verification process prevents material degradation when products move from a humid manufacturing environment to a drier destination climate.
- Digital pin-type moisture meter readings.
- Testing of various components like legs and tabletops.
- Verification against the destination climate profile.
What determines the grade of metal components?
The structural performance of residential furniture often depends on the gauge and alloy composition of internal frames or legs. Inspectors utilize salt spray tests and thickness calipers to confirm that metal parts are resistant to corrosion and capable of supporting intended weights.
- Caliper measurement of tube wall thickness.
- Coating thickness gauge for powder-coated finishes.
- Analysis of weld penetration and smoothness.
How are fabric and foam quality assessed?
Upholstery must be scrutinized for rub count resistance and flame retardancy to ensure it meets both durability and safety mandates. The checklist includes checks for “crocking” (color transfer) and density verification of the foam padding to prevent premature sagging.
- Martindale rub test for fabric abrasion.
- Smolder resistance tests for fire safety.
- Foam density checks via indentation force deflection.
Key Takeaway: Material verification is the most critical preventative measure against environmental degradation and structural weakening in finished furniture products.
| Material Type | Primary Test | Acceptable Range/Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Solid Wood | Moisture Meter | 8% – 12% (climate dependent) |
| Carbon Steel | Coating Thickness | 60 – 80 microns (standard) |
| Upholstery | Martindale Test | 20,000+ rubs for commercial use |
By rigorously analyzing these material properties, procurement teams can guarantee that the aesthetic appeal of the furniture is matched by its physical longevity.
IV. Structural Stability and Load Testing Protocols
Joint construction determines whether a bed frame or chair will collapse under the weight of a user, making static load testing mandatory. This process involves placing a heavy weight—often double the rated capacity—on the item for a set duration to check for permanent deformation.
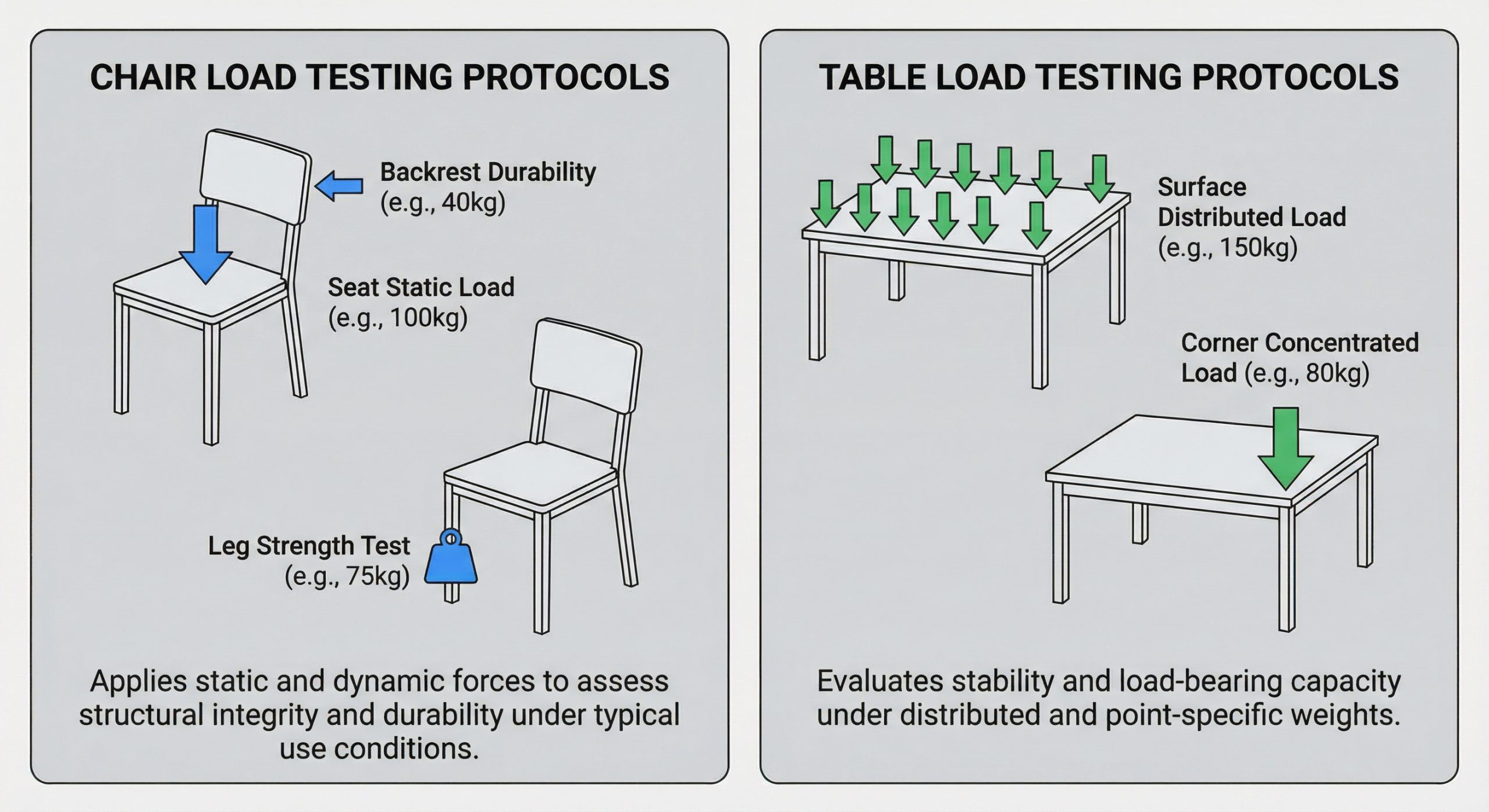
Why is static load testing mandatory?
Empirical evidence of structural integrity is provided through the application of 200kg+ loads on seating surfaces and stress testing of bed slats. These tests ensure that neither the materials nor the joinery fail under peak stress conditions common in commercial or domestic settings.
- Application of 200kg+ loads on seating surfaces.
- Stress testing of bed slats and center rails.
- Verification of weld or joint integrity post-load.
How does drop testing ensure durability?
Drop tests essential for simulating accidental falls involve dropping a weight from a specific height onto the seat or backrest to observe shock distribution. This protocol evaluates the resilience of leg-to-frame connection points and identifies weaknesses that could lead to breakage during use.
- Impact testing using a standardized “sandbag” weight.
- Evaluation of leg-to-frame connection points.
- Assessment of glass or stone inserts for shatter resistance.
What defines a successful stability test?
Stability tests determine the point at which an item will tip over by applying force to various angles of the piece. Inspectors verify that the furniture remains upright under both normal and slightly abnormal conditions to guarantee user safety.
- Rearward and sideward stability measurements.
- Evaluation of base diameter versus height ratios.
- Leveling glide adjustment range and effectiveness.
Key Takeaway: Structural testing provides empirical evidence that the furniture can withstand the rigors of daily use without compromising user safety.
| Test Name | Methodology | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Static Load | Constant weight application | No permanent deformation or cracks |
| Impact Test | Dynamic weight drop | No structural failure at joints |
| Tip-over Test | Calculated force application | Item remains stable at required angle |
The detailed examination of structural limits allows manufacturers to refine their assembly techniques and ensures that bulk orders are safe for heavy-duty environments.
V. Surface Finish and Aesthetic Standards in the Checklist
Slight variations in stain or paint batches lead to a mismatched appearance when bulk items are placed together in a single room. A furniture quality inspection checklist must include a color comparison against an “approved golden sample” under standardized lighting conditions to maintain consistency.
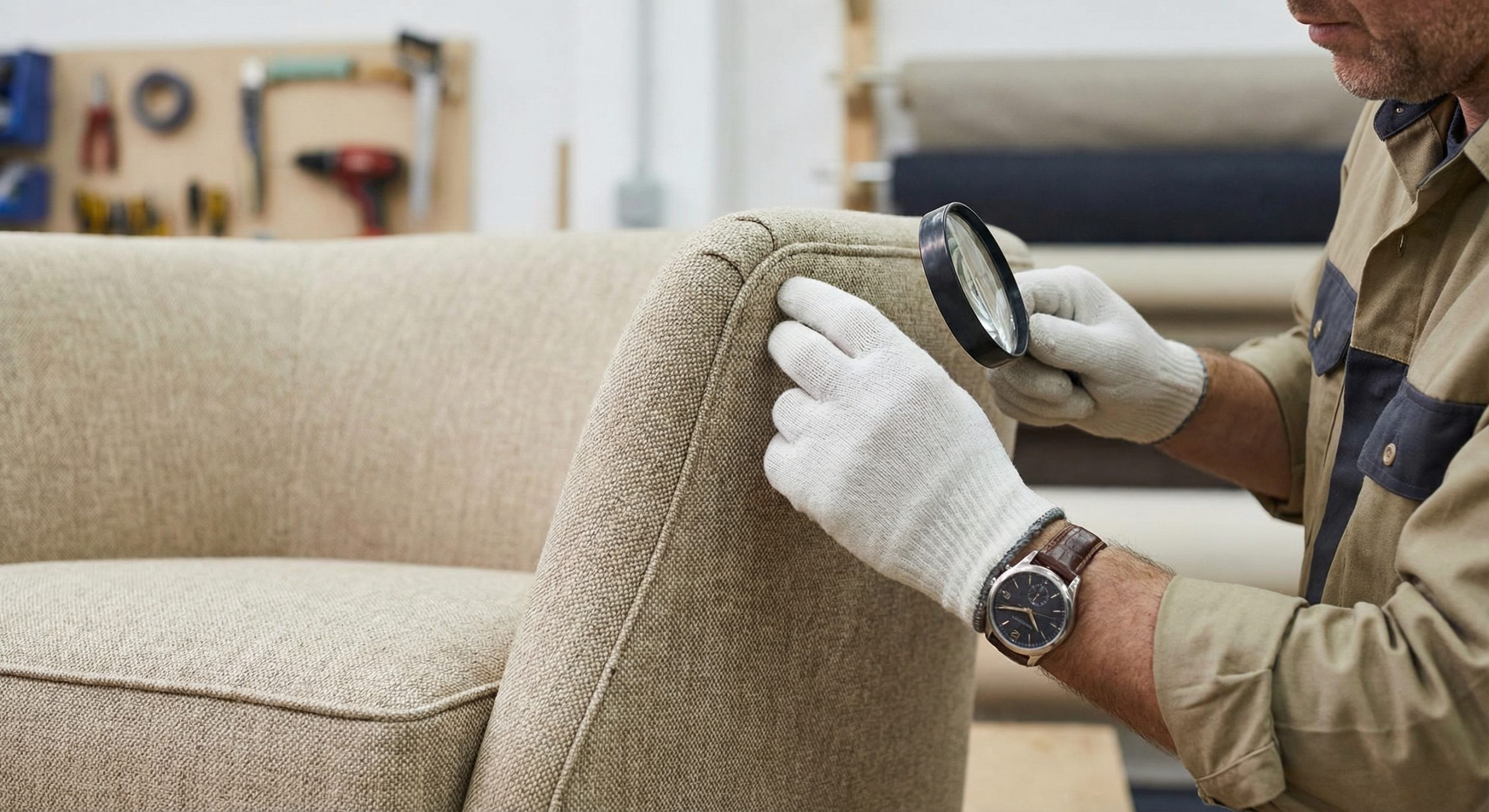

How is color consistency maintained?
Visual inspection for “runs,” “sags,” or “orange peel” is conducted alongside gloss meter readings to ensure sheen levels match specifications. Inspectors use specialized light boxes to compare finishes against Pantone standards, ensuring the entire shipment remains visually uniform.
- Use of a Light Box (D65/TL84) for color matching.
- Visual inspection for “runs,” “sags,” or “orange peel.”
- Verification of sheen levels using a gloss meter.
What constitutes a finish adhesion failure?
Finish adhesion failure occurs if paint or lacquer peels away easily, exposing the substrate to moisture and aesthetic degradation. The “cross-hatch” tape test is the industry standard for determining how well a coating adheres to the furniture surface.
- Tape pull test on a grid-scribed surface.
- Inspection for flaking at the edges of the grid.
- Rating the adhesion from 0B to 5B.
How are tactile defects categorized?
Tactile smoothness is a key metric for high-quality furniture, as rough sanding marks or hidden burrs negatively influence the user experience. Inspectors must manually check surfaces, including the undersides of tables, to detect debris trapped in the finish or unfinished areas.
- Hand-touch test for surface smoothness.
- Inspection for “dust in finish” or trapped debris.
- Checking the underside of tables for unfinished areas.
Key Takeaway: Aesthetic perfection is not merely about appearance; it is a direct indicator of the precision and care taken during the manufacturing process.
| Aesthetic Feature | Inspection Method | Rejection Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Paint/Stain | Color Match (Pantone) | Visible deviation from sample |
| Lacquer | Cross-hatch Tape Test | Any peeling or lifting of coating |
| Wood Grain | Visual Grading | Excessive knots or grain mismatch |
Ensuring surface excellence through these specific checklist items prevents the delivery of products that could diminish the perceived value of a brand or project.
VI. Regulatory Compliance and Safety Requirements
Children’s products require strict scrutiny regarding sharp edges, entrapment hazards, and chemical toxicity to ensure they are fit for purpose. Compliance with EN 71 or CPSIA is mandatory for kids-furniture to eliminate choking risks from small parts or toxic lead levels.

What are the safety rules for kids’ furniture?
Safety regulations for youth products mandate testing for “finger entrapment” zones and rigorous chemical analysis of finishes. These checks ensure that every piece is resilient to bite tests and free from harmful phthalates as required by global safety boards.
- Testing for “finger entrapment” zones in gaps.
- Lead and phthalate content analysis via lab reports.
- Bite-test resilience for edges and finishes.
How is fire safety verified for upholstery?
Fire safety regulations require that foam and fabric combinations pass “Cigarette” and “Match” tests to prevent rapid fire spread. Inspectors verify laboratory certificates and check for required fire safety labels on all upholstered seating components before shipment.
- Verification of fire safety labels and certificates.
- Review of lab testing results for foam combustion.
- Inspection of inter-liner materials in seating.
Which chemical emissions are restricted?
Formaldehyde and other VOCs emitted by engineered woods like MDF must stay below strict thresholds to protect indoor air quality. Adherence to CARB Phase 2 or EPA TSCA Title VI is verified through manufacturer test reports and on-site air sampling tests.
- Review of manufacturer emission test reports.
- Verification of “California 93120” compliance markings.
- On-site VOC “sniff” or air sampling tests.
Key Takeaway: Compliance is a mandatory prerequisite for legal trade, serving as a shield against regulatory fines and consumer safety litigations.
| Regulation | Scope | Core Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| EN 71-3 | Children’s Safety | Migration of certain chemical elements |
| TB 117-2013 | Upholstery Fire | Smolder resistance of filling materials |
| CARB Phase 2 | Formaldehyde | Strict emission limits for composite wood |
By integrating these regulatory checkpoints into the inspection process, businesses ensure their bulk orders are fit for purpose and legally compliant in their target markets.
VII. Operational Functionality in the Furniture Quality Inspection Checklist
Moving parts such as drawer slides, door hinges, and height-adjustment levers must operate smoothly without excessive noise or resistance. The furniture quality inspection checklist requires a “cycle test” where these components are opened and closed dozens of times to ensure they remain secure.

How are moving parts tested for longevity?
A standard 50-cycle test for drawers and cabinet doors identifies potential mechanical failures or misalignments in handles and pulls. Inspectors also verify the timing of “soft-close” mechanisms to ensure consistent operational quality across the entire batch.
- 50-cycle test for drawers and cabinet doors.
- Verification of “soft-close” mechanism timing.
- Checking for alignment of handles and pulls.
What defines a successful assembly check?
A successful assembly check involves physically building a randomly selected “knock-down” unit to ensure all pre-drilled holes align perfectly. This step identifies critical hardware omissions and confirms that instruction manuals are clear enough for the end customer to follow.
- Full assembly of a randomly selected unit.
- Verification of instruction manual clarity.
- Assessment of hardware “spare parts” inclusion.
How is electrical integration verified?
Voltage and amperage checks for built-in USB ports are mandatory for modern furniture featuring integrated charging solutions. Inspectors must also confirm that all internal wiring is properly insulated and routed to prevent pinching or grounding failures in metal frames.
- Voltage and amperage checks for USB ports.
- Grounding continuity tests for metal frames.
- Inspection of cable routing to prevent pinching.
Key Takeaway: Functionality testing ensures that the furniture performs its intended role reliably, enhancing the end-user’s overall satisfaction.
| Component | Test Action | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|
| Drawer Slides | 50 Full Extensions | Smooth motion, no snagging |
| KD Hardware | Trial Assembly | All holes align, hardware fits |
| Power Ports | Multi-device Charge | Consistent power delivery |
This functional deep-dive prevents the shipment of units that may look perfect but fail to operate correctly once they reach the customer.
VIII. Dimensions and Tolerance Specifications
Discrepancies as small as 5mm in height can prevent a chair from fitting under a desk or create an uneven table surface. Inspectors utilize steel tapes and digital calipers to measure the overall width, depth, and height against technical drawings provided in the purchase order.

How are critical dimensions measured?
Steel tapes and digital calipers are used to verify seat height, armrest clearance, and the “squareness” of frames via diagonal measurements. This process ensures that every piece of furniture produced matches the engineering intent and fits correctly within the designated layout.
- Measurement of seat height and armrest clearance.
- Checking the “squareness” of frames using diagonals.
- Verification of thickness for tabletops and panels.
What is an acceptable tolerance level?
Acceptable tolerance levels define the allowable deviation in mass production, typically ranging from +/- 2mm for small parts to +/- 5mm for larger items. Any deviation exceeding these limits is marked as a “Major” defect and could lead to the rejection of the batch.
- Definition of tolerance ranges in the spec sheet.
- Marking deviations that exceed the “Major” defect limit.
- Evaluating the impact of variance on nested products.
Why is leveling a critical metric?
Leveling is critical because an uneven base is one of the most common consumer complaints in the global furniture industry. Inspectors place items on a “dead-level” steel plate and use feeler gauges to check for gaps between the legs and the floor.
- Feeler gauge test for leg gaps.
- Verification of adjustable leveler range.
- Assessment of floor protection pad attachment.
Key Takeaway: Dimensional accuracy ensures that furniture fits within its intended space and interacts correctly with other pieces in a set.
| Dimension Type | Tool Used | Standard Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Height | Steel Tape | +/- 3mm to 5mm |
| Panel Thickness | Digital Caliper | +/- 0.5mm to 1.0mm |
| Diagonal Square | Laser/Tape | < 2mm difference |
By enforcing strict dimensional controls, procurement officers avoid the logistical nightmare of furniture that is incompatible with the design layout of a project.
IX. Packaging and Logistics in the Furniture Quality Inspection Checklist
Carton strength must be sufficient to withstand the pressures of container shipping to avoid ruining high-quality furniture during transit. The furniture quality inspection checklist includes a “bursting test” for the cardboard and a check of the “Edge Crush Test” (ECT) rating.

How is carton strength verified?
Carton strength is verified through the inspection of double-wall corrugated cardboard and the use of humidity-resistant glue. Ensuring an ECT 32 or ECT 44 rating guarantees that cartons can be stacked safely without collapsing under the weight of the shipment.
- Verification of ECT 32 or ECT 44 ratings.
- Inspection of double-wall corrugated cardboard.
- Checking for humidity-resistant glue in cartons.
What does the ISTA drop test reveal?
The ISTA drop test simulates the rough handling that occurs in ports and during last-mile delivery, ensuring the outdoor furniture inside remains undamaged. Fully packed boxes are dropped from various heights onto their edges and corners to identify potential internal component shifts or foam breakage.
- 10-point drop test following ISTA 1A or 2A.
- Post-test inspection for internal component shifts.
- Checking for “foam compression” or breakage.
Why is marking and labeling checked?
Incorrect labeling leads to customs delays and lost inventory, making accurate barcode and “Country of Origin” markings essential. Inspectors verify that all “Team Lift” and “Fragile” warnings are clearly visible and that the carton information matches the shipping manifest.
- Barcode scannability check with a handheld reader.
- Verification of “Team Lift” or “Weight” warnings.
- Checking the accuracy of the PO number and SKU.
Key Takeaway: Logistics-focused inspection ensures that the product’s quality is preserved from the factory door to the final destination.
| Logistics Check | Method | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Carton Drop | ISTA 1A Protocol | Zero damage to internal product |
| Markings | Visual/Scanner | 100% accuracy of labels/barcodes |
| Internal Packing | Component Wrap | Prevent scratching during vibration |
By focusing on the protection of the goods during transit, the checklist significantly reduces the rate of shipping-related insurance claims.
X. Professional Execution of a Furniture Quality Inspection Checklist
Inspecting every single unit in a 10,000-piece order is impractical, so professionals use the “AQL” standard to determine a representative sample size. This statistically significant selection allows inspectors to accurately assess the quality of the entire batch without checking every item.
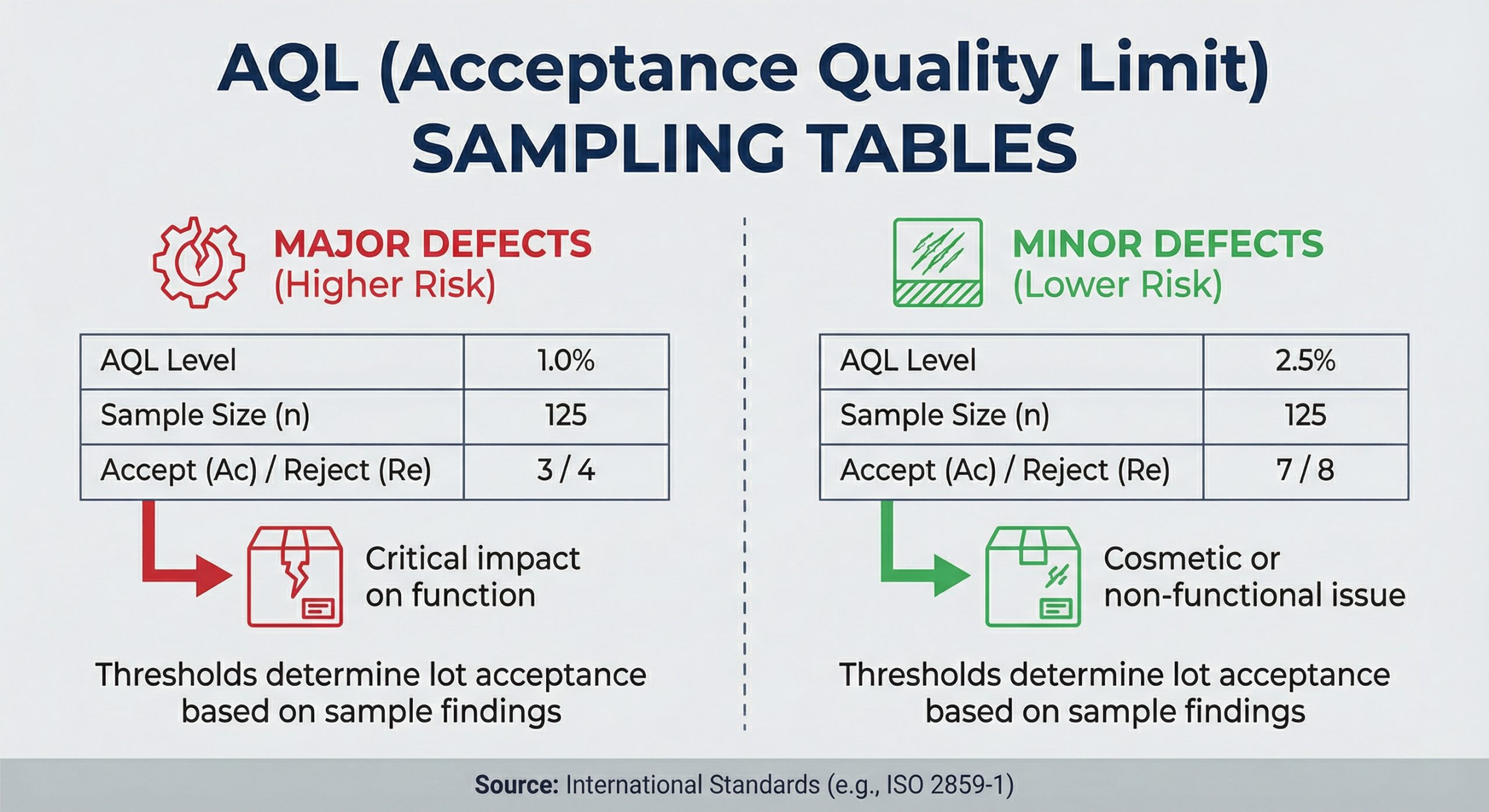
How are sample sizes determined?
Statistical validity is maintained by using AQL Level II tables (ISO 2859-1) to determine how many cartons must be randomly selected. This method provides a clear “Pass/Fail” threshold based on the number of critical, major, and minor defects found within the sample.
- Use of AQL Level II for general inspections.
- Random selection of cartons from all parts of the pile.
- Determination of “Pass/Fail” based on defect counts.
What tools are essential for the inspector?
Essential tools for furniture analysis include calibrated digital calipers, moisture meters, gloss meters, and Pantone color books. Inspectors also carry specialized “entrapment probes” to conduct mandatory safety checks for products aimed at the youth and domestic markets.
- Digital calipers and 5-meter steel tapes.
- RAL or Pantone color matching books.
- Specialized “entrapment probes” for safety checks.
How is the final report structured?
The final report provides the buyer with evidence-based photo documentation and a detailed breakdown of all identified failures. It concludes with a clear “Pass,” “Fail,” or “Pending” status, serving as the definitive decision-making tool for shipment approval.
- Clear “Pass,” “Fail,” or “Pending” status.
- Evidence-based photo documentation of failures.
- Detailed breakdown of critical vs. minor issues.
Key Takeaway: Professional execution transforms a simple list into a powerful decision-making tool that mitigates financial risk in bulk procurement.
| Inspection Factor | Professional Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | AQL Tables (ISO 2859) | Statistical validity of findings |
| Color Accuracy | Pantone Bridge Guide | Objective color verification |
| Transparency | Digital Inspection Report | Final decision support for buyer |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1.Can I modify the checklist for different types of materials?
The checklist should be a living document that adapts to solid wood, metal-framed, or upholstered items. Each material requires specialized tests, such as moisture checks for timber or salt-spray tests for metals.
Q2. What’s the most common defect found in bulk furniture orders?
Surface finish issues and dimensional discrepancies are the most frequent problems identified during inspections. These often stem from environmental factors in the factory or calibration errors in CNC machinery.
Q3. Can I use the checklist for small-batch artisanal orders?
Principles of material integrity and structural safety apply to any volume, though artisanal orders may focus more on craftsmanship. For smaller batches, the focus shifts from statistical AQL averages to individual piece perfection.
Q4. What happens if the factory fails the inspection?
A failure typically triggers a “re-work” process where the factory must fix identified defects at their own expense. A second inspection is scheduled to verify corrections meet standards before the goods are released.
Q5. Is a factory’s internal QC enough for a bulk order?
Internal QC teams are often under pressure to meet deadlines, which can lead to oversight of critical defects. Independent third-party inspection provides an unbiased layer of protection that internal teams cannot always guarantee.
Conclusion: Securing the Future of Furniture Procurement
In the high-stakes world of B2B procurement, a furniture quality inspection checklist is not just a document; it is a strategic asset. By systematically addressing material integrity, structural safety, and logistical readiness, organizations can ensure that their bulk orders are a source of value rather than a liability. As global supply chains become more complex and consumer expectations for durability and safety rise, the reliance on data-driven quality control will only increase.
We invite you to explore our approach to furniture manufacturing, where quality is integrated into every step of the process. The future of the industry belongs to those who view inspection not as a hurdle, but as a commitment to excellence and a guarantee of long-term partnership success. By adopting these rigorous standards, you secure your brand’s reputation and ensure that every piece of furniture delivered is a testament to quality craftsmanship.
